The easiest way to begin is with the numbers.
Some 60 years ago today, at 11:02 in the morning, the American B-29 bomber dropped a 10,200 pound plutonium bomb (nicknamed Fat Man
) over the city of Nagasaki, a tourist destination, industrial center and sea-port in southwestern Japan with a population of about 230,000. The bomb exploded about 500 yards above Nagasaki, creating a fireball, a shockwave, and a massive burst of radiation. Some 74,000 civilians — about 1/3 of the population of Nagasaki — were burned alive, crushed to death by the shockwave, or sickened and died over the next few months due to severe radiation poisoning (the burning away of their internal organs by intense radiation) and cancer.
Three days before, with no prior warning, a B-29 bomber had dropped an enriched uranium bomb over Hiroshima, an industrial center in western Japan, with a population of about 255,000. The bomb had exploded about 670 yards above the city. 80,000 civilians were burned alive or crushed to death by the explosion. By the end of 1945, another 60,000 people died due to severe radiation poisoning and cancer, raising the death toll to about 140,000–about 55% of the city’s population.
One of the reasons that Hiroshima and Nagasaki were chosen as targets is that they were considered to be good sites to demonstrate the killing power of the Bomb: they had been mostly untouched during the six months of low-altitude firebombing of Japanese cities. The first major raid of that campaign was the firebombing of Tokyo in the middle of the night on March 9-10, 1945. 334 American B-29 bombers raced over the city at about 7,000 feet, and dropped about 1,700 tons of napalm bombs. It is estimated that about 100,000 civilians were burned to death in one (1) night. Over the next 6 months, from March 10 to Japan’s surrender on August 15, over 100 Japanese cities were firebombed; about 500,000 civilians were burned to death.
All told, the firebombing and nuclear attacks and conventional
air raids on Japan killed somewhere between 800,000 and 1,000,000 Japanese civilians over the course of half a year.
Then there are the names.

Curtis LeMay

Henry L. Stimson, Secretary of War

Harry Truman, President
The B-29 Bockscar
, which incinerated one third of the people of Nagasaki, was piloted by Major Charles Sweeney. The actual dropping of the bomb was carried out by the plane’s bombadier, Captain Kermit Beahan.
The B-29 Enola Gay
, which incinerated over half of the people of Hiroshima, was piloted and commanded by Colonel Paul Tibbets. The plane’s bombadier, Major Thomas Ferebee, dropped the bomb over Hiroshima.
Sweeney, Beahan, Tibbets, and Ferebee were members of the XXI Bomber Command, directed General Curtis LeMay. LeMay opposed the nuclear attacks, but he directed it under orders from Secretary of War Henry L. Stimson and President Harry S. Truman, who had made the decision to use atomic weapons in order to terrorize Japan into unconditional surrender. LeMay was also the architect of the low-altitude firebombing campaign, acting on advice and research from his subordinate, Lt. Col. Robert McNamara.
We will never know the names of most of the 1,000,000 or so civilians who were killed in the onslaught. The Japanese government was in disarray in the closing months of the war, and many of the records were consumed by the flames along with the lives of the victims.
Then there are the statements of intent.
The purposes of the bombing was to achieve victory through catastrophic bloodshed and terror. LeMay, when asked about his bombing campaigns, stated There are no innocent civilians, so it doesn’t bother me so much to be killing innocent bystanders.
(He also mused, later, I suppose if I had lost the war, I would have been tried as a war criminal.
) The interim committee deciding to drop the bomb stated, on May 31, 1945, that we could not give the Japanese any warning
before the atomic bombing of Hiroshima. About 24 hours before the incineration of Nagasaki, U.S. planes began dropping leaflets all over Japan, threatening more destruction but naming no targets that could be evacuated. The leaflets did not reach Nagasaki at all until August 10, the day after it was destroyed. The leaflets read:
TO THE JAPANESE PEOPLE:
America asks that you take immediate heed of what we say on this
leaflet.
We are in possession of the most destructive explosive ever devised
by man. A single one of our newly developed atomic bombs is
actually the equivalent in explosive power to what 2000 of our
giant B-29s can carry on a single mission. This awful fact is one
for you to ponder and we solemnly assure you it is grimly accurate.
We have just begun to use this weapon against your homeland. If you
still have any doubt, make inquiry as to what happened to Hiroshima
when just one atomic bomb fell on that city.
Before using this bomb to destroy every resource of the military by
which they are prolonging this useless war, we ask that you now
petition the Emperor to end the war. Our president has outlined for
you the thirteen consequences of an honorable surrender. We urge
that you accept these consequences and begin the work of building a
new, better and peace-loving Japan.
You should take steps now to cease military resistance. Otherwise,
we shall resolutely employ this bomb and all our other superior
weapons to promptly and forcefully end the war.
Shortly before the leaflets were dropped, Harry Truman also publicly declared his aims: It was to spare the Japanese people from utter destruction that the ultimatum of July 26 was issued at Potsdam. Their leaders promptly rejected that ultimatum. If they do not now accept our terms, they may expect a rain of ruin from the air the likes of which has never been seen on this earth.
Of course, no specific warning was given to the civilians of Nagasaki, at any point.
After the war, Truman defended his decision to burn nearly 1,000,000 civilians to death on the grounds that it was necessary to secure the unconditional submission of Japan to surrender and occupation without a costly marine invasion of the home islands.
Then there are the effects. For most of these there are no words.

Aftermath of the Tokyo firebombing, 10 March 1945

Aftermath of the atomic bombing of Hiroshima, 6 August 1945
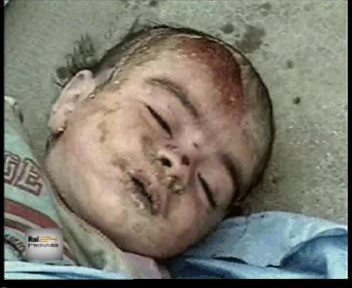
A boy caught by the bombing in Hiroshima

The explosion and mushroom cloud, seen from ground level in Nagasaki on 9 August 1945.

Nagasaki railroad station

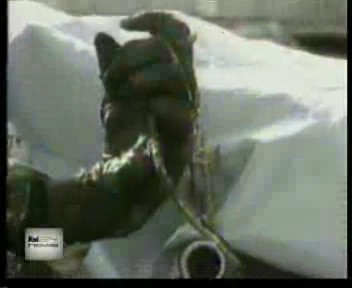
A clock from Nagasaki, stopped at 11:02 AM
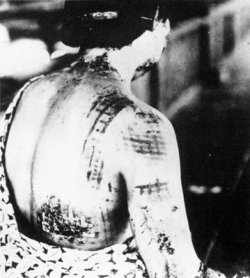
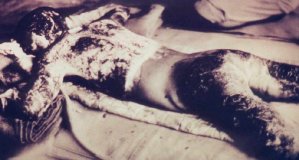
A woman caught by the bombing in Nagasaki

Iwakawa-machi residential neighborhood, Nagasaki
Here are some facts you do not need to remind me of today: that the government of the Empire of Japan launched a war of aggression against American territory and killed both American military and civilians; that they conducted a brutal war of conquest against China in which hundreds of thousands of civilians were mercilessly tortured and killed; that some fanatical elements of the military regime wanted to fight the United States down to the last man. That’s all true, but it’s quite beyond the point. None of these vicious acts by a vicious government justifies doing this to people, to civilians who had no meaningful role in either the decision-making or in the fighting. Nothing could. If you want to make a plea on behalf of terror-bombing, fine; do so. But not here. I’ll post again tomorrow or in a couple days, and we can argue there about the merits and demerits of burning 1,000,000 innocent people alive when you think you can get good results from it. But for now, the dead deserve at least a day of quiet mourning.
Today there’s a memorial for the victims standing in the Hiroshima Peace Park, with an inscription that reads Rest in peace, for this mistake will not be repeated.
Let us remember the dead, and pray that those words are true.
Further reading