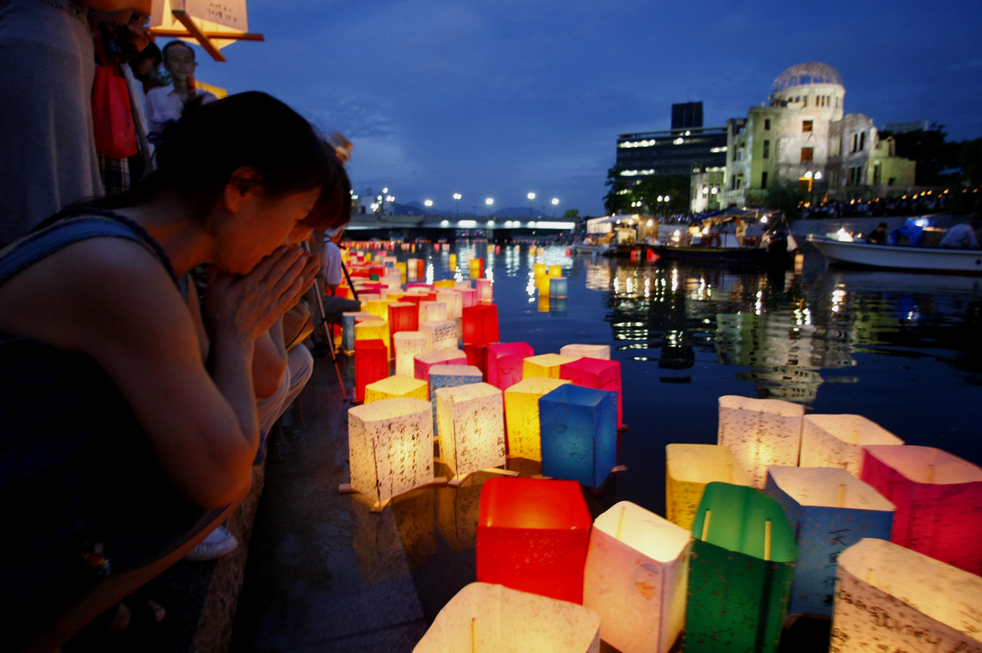
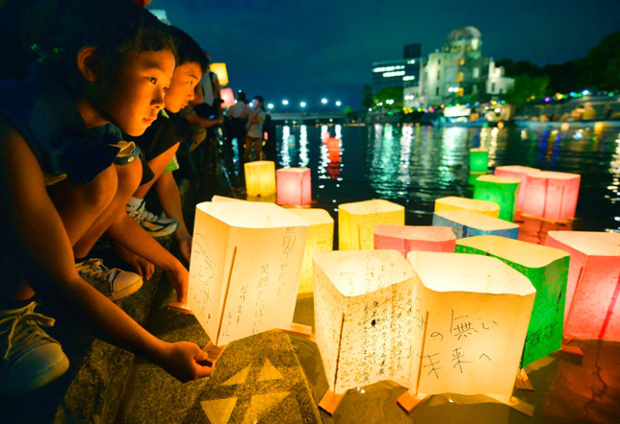
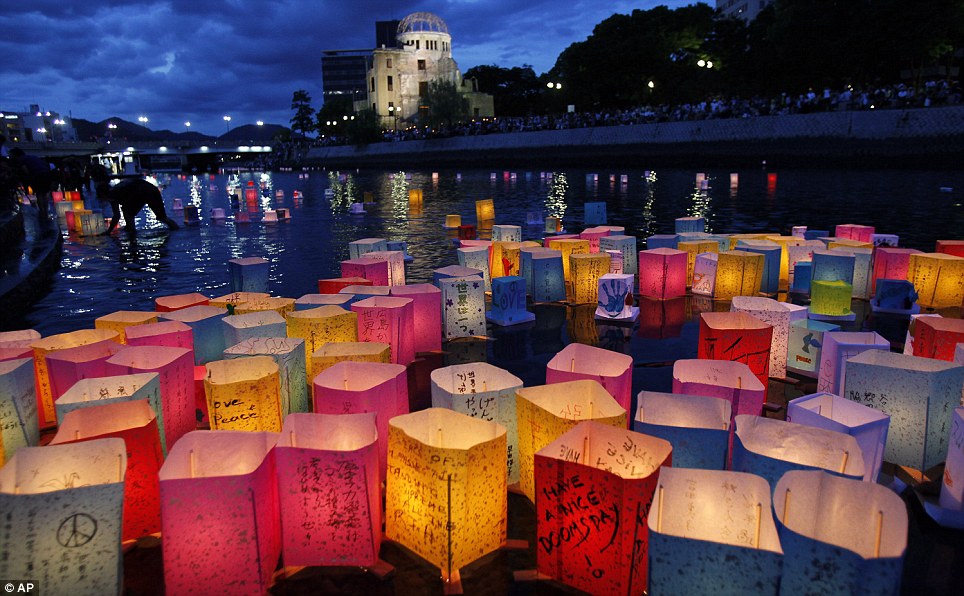
8:15am. 73 years, 140,000 souls.

Donated by Kazuo Nikawa
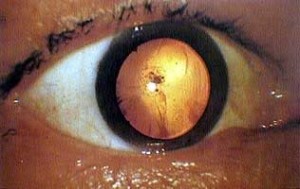
1,600m from the hypocenter
Kan-on BridgeKengo Nikawa (then, 59) was exposed to the bomb crossing the Kan-on Bridge by bike going from his home to his assigned building demolition site in the center of the city. He suffered major burns on his right shoulder, back, and head and took refuge in Kochi-mura Saiki-gun. He died on August 22. Kengo was never without this precious watch given him by his son, Kazuo.
Seventy-three years ago today, on August 6, 1945, between 8:15 and 8:16 in the morning, the American B-29 bomber Enola Gay
dropped an atomic bomb over Hiroshima, Japan. The government of the United States chose Hiroshima as their target because it was still standing. For half a year, the U.S. government had waged a war of unrelenting, devastating low-altitude firebombing of cities throughout the Japanese home island. Within six months, the firebombing had killed hundreds of thousands of Japanese civilians. The firebombing had destroyed over 60 Japanese cities. Hiroshima was still mostly undamaged. So they believed that would make it a good place to test the effects of the new atom bomb. And Hiroshima became the first city ever attacked with nuclear weapons in the history of the world.
It would not be the last.
On a bright morning in August, without warning, the B-29 dropped its atom bomb over the densely-populated center of the city. The bomb exploded about 2,000 feet above ground. And it created a 13 kiloton explosion, a fireball, a shock-wave, and a burst of radiation. On the day that the bomb was dropped, there were somewhere around 255,000-300,000 people living in Hiroshima.
There was a sudden flash, brighter than the sun, and then sky went dark, buildings were thrown to the ground, and everything began to burn. People were burned alive and nothing left but a shadow on the wall. People staggered through the ruins, their eyes blinded, their clothing burned off their bodies, skin burned off in the heat.
Everyone was desperate for water, everything was unbearably hot. They begged soldiers for water from their canteens; they drowned themselves in cisterns. Later, black rain began to fall from the darkened sky. And the people escaping from the city center thought it was a miracle. They tried to catch the rain on their tongues, or they caught it and drank it out of cups. They didn’t know that the rain was fallout. They didn’t know that it was full of radiation and as they drank it it was burning them away from the inside. There was no refuge, no sanctuary. There was nobody to help. The city was burning. The doctors and nurses were almost all downtown when the bomb hit. The atom bomb exploded directly over one of the major clinics, and over 90% of the doctors, and over 90% of the nurses, were killed or injured in the bombing.
Because the U.S. bomber targeted the city center, about 85% of the people killed in Hiroshima were civilians.
The explosion completely incinerated everything within a one mile radius of the city center. The shock-wave and the fires ignited by the explosion damaged or completely destroyed about nine-tenths of the buildings in the city. Somewhere between 70,000 and 80,000 people–or, about one quarter to one third of the entire population of the city–died immediately. The heat of the explosion vaporized or carbonized the children and adults who were nearest to Ground Zero when the bomb went off.
Thousands more were further away from the center, and they died when they were crushed to death by the force of the shock-wave, when they were burned by the blast or by the fires raging throughout the ruined city, when they were trapped underneath collapsing buildings or when they drowned in the river as they tried to escape. They died from dehydration; they were killed quickly or slowly by radiation poisoning and infections and cancers that ate their bodies away from the inside out. Some died suddenly, and some died slow, lingering, painful and unavoidable deaths over days or weeks. It is estimated that in all, the atomic bombing killed about 130,000-140,000 people. It left thousands more with permanent disabilities from their injuries and from the radiation that spread in a burst and spread through the fallout.
Almost all of the people who were maimed and killed in the obliteration of the city were civilians.
Although there were some minor military bases near Hiroshima, the bomb was dropped on the city center, several miles away from the military bases on the edge of town. Hiroshima was chosen as a target, even though it had little military importance, because It is a good radar target and it is such a size that a large part of the city could be extensively damaged. There are adjacent hills which are likely to produce a focussing effect which would considerably increase the blast damage.
1. And it was one of the cities still standing after the American firebombing campaign. U.S. military planners believed it strategically important to demonstrate as much destruction as possible from the blast.
Thomas Ferebee, a bombadier for the United States Army, was the man who dropped the atomic bomb on Hiroshima. His commanding officer was the pilot of the Enola Gay, Paul Tibbets. Tibbets and Ferebee were part of the XXI Bomber Command, directed by Curtis LeMay. LeMay planned and executed the atomic bombings at the behest of Secretary of War Henry L. Stimson and President Harry Truman.
Kengo Nikawa died on August 22nd, 1945 because of the bombing. This is his pocket watch.
We will never know the names of many of the 140,000 other residents of Hiroshima who were killed by the bombing. We have only estimates because the Japanese government was already in a shambles by this point in the war, and countless records, of those that were successfully kept, were consumed by the flames, along with the people whose lives they recorded.
Three days later, on August 9, 1945, CBS broadcast a recorded address by President Harry S. Truman about the atomic bombing. It was broadcast on the same day that the government of the United States sent bombers to Nagasaki to incinerate a second city, with a second atomic bomb. Here is what Truman said:

Harry S. Truman, August 9, 1945.
We won the race of discovery against the Germans….
In his radio address on August 9, Truman disingenuously described Hiroshima, a densely populated, industrialized port city of a quarter million souls, as a military base,
and then he said, That was because we wished in this first attack to avoid, insofar as possible, the killing of civilians.
That was a lie. The bomb was dropped on the city center, over a hospital, far away from military installations.

Having found the bomb, we have used it.


… on Hiroshima, a military base…



We wished in this first attack to avoid, insofar as possible, the killing of civilians.

We have used it against those who attacked us without warning at Pearl Harbor …


We have used it … against those who starved and beaten and executed American prisoners of war …




We have used it in order to shorten the agony of war.

It is worth remembering that the atomic bombing of the Hiroshima city center — the first use of atomic weapons against human targets in the history of the world — a bombing in which the United States government’s forces deliberately targeted a civilian center — a bombing that the United States government carried out with the explicit intention of obliterating an entire city in seconds, in order to break enemy morale
— an attack in which that government’s forces deliberately turned weapons on civilians that destroyed 90% of an industrial metropolis, and killed between a third and a half of all the people living in it — was, and remains, the deadliest act of terrorism in the history of the human world.
And there are other facts, and other stories, also, that you do not need to remind me of today: of course it’s a fact that the government of the Empire of Japan launched a war of aggression against American territory and killed both American military and civilians; and it’s a fact that they conducted brutal wars of conquest against China, Korea, and throughout southeast Asia, in which hundreds of thousands of civilians were mercilessly tortured and killed; and even that down to the very end, some fanatical elements of the military regime wanted to fight the United States down to the last man.
That's all true, but it's quite beyond the point. None of these vicious acts by a vicious government justifies doing this to Japanese people, to civilian men, women and children who had no meaningful role in either the decision-making or in the fighting. No crime or atrocity of the Japanese government excuses a half-year campaign of terror against Japanese cities; no political objective could possibly allow the U.S. government to seek victory by burning 140,000 civilians alive in a single day. No strategic necessity justifies turning such weapons on a city of 300,000 human beings; no need or desire or exigency of war justifies treating 140,000 souls like this.
Nothing ever could.
in the annual August 6 memorial event, in memory of the lives lost.
Also.
- GT 2005-08-09: A day that will live in infamy
- Eric Laursen, Commentary, Agency (2015-08-05): On the Anniversary of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
- Ralph Raico, Antiwar.com (2009-08-05): Hiroshima and Nagasaki
- John Pilger (2010-08-06): The Lies of Hiroshima Are The Lies of Today
- Design Observer (November, 2008): Hiroshima: The Lost Photographs
- Hiroshima, the pictures they didn’t want us to see
The audio clip above is from a recording of President Harry S. Truman’s radio report on the Potsdam conference, recorded by CBS on August 9, 1945 in the White House. The song linked to above is a recording of Oppenheimer (1997), by the British composer Jocelyn Pook. The voice that you hear at the beginning is Robert Oppenheimer, in an interview many years after the war, talking about his thoughts at the Trinity test
, the first explosion of an atomic bomb in the history of the world, on July 16th, 1945.



