8:15am

Donated by Kazuo Nikawa
1,600m from the hypocenter
Kan-on BridgeKengo Nikawa (then, 59) was exposed to the bomb crossing the Kan-on Bridge by bike going from his home to his assigned building demolition site in the center of the city. He suffered major burns on his right shoulder, back, and head and took refuge in Kochi-mura Saiki-gun. He died on August 22. Kengo was never without this precious watch given him by his son, Kazuo.
Sixty seven years ago today, on August 6, 1945, at 8:15 in the morning, the American B-29 bomber Enola Gay
dropped an atomic bomb over the center of the city of Hiroshima, Japan. Hiroshima was the first target ever attacked with nuclear weapons in the history of the world.
The bomb exploded about 200 yards over the city, creating a 13 kiloton explosion, a fireball, a shock-wave, and a burst of radiation. On the day that the bomb was dropped, there were about 255,000 people living in Hiroshima.
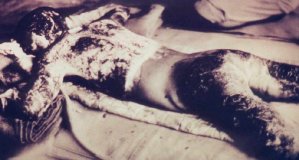
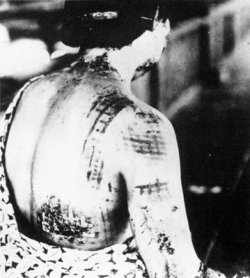
The explosion completely incinerated everything within a one mile radius of the city center. The shock-wave and the fires ignited by the explosion damaged or completely destroyed about nine-tenths of the buildings in the city. Somewhere between 70,000 and 80,000 people–that is, about one third of the entire population of the city–died immediately. The heat of the explosion vaporized or burned alive many of those closest to ground zero. Others were killed by the force of the shock-wave or crushed under collapsing buildings. Many more died from acute radiation poisoning
–that is, from the effects of having their internal organs burned away in the intense radiation from the blast.
By December 1945, thousands more had died from their injuries, from radiation poisoning, or from cancers related to the radioactive burst or the fallout. It is estimated that the atomic bombing killed about 140,000 people, and left thousands more with permanent disabilities.
Almost all of the people maimed and killed were civilians. Although there were some minor military bases near Hiroshima, the bomb was dropped on the city center, several miles away from the military bases on the edge of town. Hiroshima was chosen as a target, even though it had little military importance, because It is a good radar target and it is such a size that a large part of the city could be extensively damaged. There are adjacent hills which are likely to produce a focussing effect which would considerably increase the blast damage.
1. Hiroshima was also one of the largest Japanese cities not yet damaged by the American firebombing campaign. Military planners believed it strategically important to demonstrate as much destruction as possible from the blast.
Thomas Ferebee, a bombadier for the United States Army, was the man who dropped the atomic bomb on Hiroshima. His commanding officer was the pilot of the Enola Gay, Paul Tibbets. Tibbets and Ferebee were part of the XXI Bomber Command, directed by Curtis LeMay. LeMay planned and executed the atomic bombings at the behest of Secretary of War Henry L. Stimson and President Harry Truman.
Kengo Nikawa died on August 22nd, 1945 because of the bombing. This is his pocket watch.
We will never know the names of many of the 140,000 other residents of Hiroshima who were killed by the bombing. We have only estimates because the Japanese government was in a shambles by this point in the war, and countless records, of those that were successfully kept, were consumed by the flames, along with the people whose lives they recorded.
The late, great Utah Phillips called this one of the first songs he ever wrote that ever made any sense. It’s certainly one of his best.
Enola Gay
Look out, look out
from your school room window
Look up young children from your play
Wave your hand
at the shining airplane
Such a beautiful sight is Enola GayIt's many a mile
from the Utah desert
To Tinian Island far away
A standing guard
by the barbed wire fences
That hide the secret of Enola GayHigh above the clouds
in the sunlit silence
So peaceful here I'd like to stay
There's many a pilot
who'd swap his pension
For a chance to fly Enola GayWhat is that sound
high above my city
I rush outside and search the sky
Now we are running
to find our shelter
The air raid sirens start to cryWhat will I say
when my children ask me
Where was I flying upon that day?
With trembling voice
I gave the order
To the bombardier of Enola GayLook out, look out
from your school room window
Look up young children from your play
Your bright young eyes
will turn to ashes
In the blinding light of Enola Gay I turn to see
the fireball rising
My god, my godall I can say
I hear a voice
within me crying
My mother's name was Enola GayLook out, look out
from your school room window
Look up young children from your play
Oh when you see
the war planes flying
Each one is named Enola Gay.–U. Utah Phillips (1994), on I’ve Got To Know
It is worth remembering that the atomic bombing of the Hiroshima city center — a bombing in which forces acting on behalf of the United States government deliberately targeted a civilian center, in order to break enemy morale,
and in which they killed over half of all the people living in an industrial metropolis — remains the deadliest act of terrorism in the history of the world.